
The article describes the result of biological and clinical protective effects of the peptide IPH AVN. The application of the peptide IPH AVN significantly increases in human cell culture “cascade” of signal molecules, which is necessary for the activation of proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in the cells of the vascular system, the formation of vascular system, regulation of metabolism in epithelial cells, regulation of blood vessel tone, smooth muscle of the vascular wall and thrombosis. The application of the peptide IPH AVN has a pronounced angioprotective nature in cell culture. The application of the peptide IPH AVN promotes the reparation of the arterial system after damage, reduce clot formation on the basis of these experimental models. The application of the peptide IPH AVN leads to the optimization of vascular function and improvement of peripheral hemodynamics. The application of the peptide IPH AVN improves the elasticity of the vascular wall, leads to the optimization of the functional activity of the peripheral blood circulation system according to clinical study.
The study of the effects of peptides has a great interest today. Peptides have the same structure as proteins, but the size of these molecules is smaller. It is also important that short peptides are a natural metabolic product in the body and they can`t be detected in blood or urine. That’s why, it is interesting to study the effects of peptides on cell cultures [1, 2, 3].
The peptide IPH AVN contains a low molecular weight peptide, it has angio – and vasoprotective properties and has a normalizing effect on the vascular system [3, 4].
The results of experimental studies have shown that the peptide IPH AVN regulates metabolic processes in blood vessels, reduces the permeability of the vascular wall, increases the reserve capacity of the body, which suggests the effectiveness of the peptide IPH AVN to normalize the functions of the human vascular system in disorders of various origins [1, 5].
The aim of this study was to identify biological and clinical angioprotective effects of the peptide IPH AVN.
Material and methods.
We conducted 3 areas of research to identify the biological and clinical effects of the peptide IPH AVN:
In a cell-based study we selected embryonic stem cells to study the cytostatic, geroprotective and oncoprotective properties of the peptide IPH AVN in relation to the vascular system. These cells belong to the pluripotent type, which means that they can be differentiated into all three primary germ sheets: ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm. Organs and glands of the vascular and other systems are formed from these primary germ sheets in the future. The human embryo transformes the blastocyst stage in 5-6 days after fertilization. The stem cells are obtained from the blastocyst.
We carried out the genes responsible for the formation of the vascular system make up a complex of ACE, AGT, AGTR2, NOS3, MTHFR genes. ACE gene (angiotensin-1 converting enzyme ACE) is mapped in 17q23 locus. AGT and AGTR1 GENES, which encode angiotensinogen and receptor type 1 to angiotensin II, and the product of the gene NOS3 NOsynthase is a key enzyme in the regulation of blood vessel tone, smooth muscle of the vascular wall and thrombosis. The methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene regulates homocysteine metabolism in the cell. NOS3 and MTHFR gene polymorphisms are associated with predisposition to cardiovascular disease. In connection with these data, we decided to study the activity of this complex of genes in the application of the peptide IPH AVN. We also assessed the biological active markers. We used immunofluorescence technique using primary antibodies to VEGF protein (1:250, Abcam), p53 (1:50, Abcam). VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) is a signaling protein produced by cells to stimulate vasculogenesis (formation of the embryonic vascular system) and angiogenesis (growth of new vessels in the already existing vascular system). Aging of polypotent cells in culture is associated with increased activity of the p53 gene. Protein p53 is activated by DNA damage or is a signal of aging cells and violation of their functional activity. P53-dependent apoptosis avoids the accumulation of mutations, and, in the case where they have already arisen, p53-dependent apoptosis allows to eliminate such potentially dangerous to the body.
We have created the following groups for the study: 1 group – the study of molecular expression before the study; 2 group-control (we added the culture medium, incubation with serum albumin); 3 group – we added the control dipeptide Glu-Trp at the concentration of 100 micrograms (mcg); 4 group – we added the peptide IPH AVN at a concentration of 100 micrograms (mcg). We selected the peptide Glu-Trp with the immune properties and well described in the literature as a control.
The PCR method was used to measure the level of gene expression using Novocasta’s reagents and sets of monoclonal antibodies produced by Biosource (Belgium). We used confocal microscope Olympus
FluoView FV1000 with indicator of 200, 400, 600. We conducted the measurement of the expression in %.
We have chosen the most commonly used species of laboratory animals for the study for the experiment recommended by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation in the Manual for preclinical studies of drugs – rats.
We created an experimental model of the muscle injury with vascular lesions in rats to study the properties of the peptide IPH AVN. In order to cause muscle injury, we introduced the drug nortexin into the quadriceps muscle of the left limb of rats, and also applied salt solutions (iron chloride) to create additional foci of thrombosis. We investigated 50 rats at the age of 14.3±1.1 month and weight 409,3±8.3 g, which created the conditions muscle injury with lesion of the arterial system. The rats were divided into 2 groups – the control (n=25) and the main group (n=25). All procedures of animal keeping and testing were carried out in accordance with standards ISO 10993-1-2003 and GOST RISO 10993.2-2006. The rats of the main group were given orally through a pipette-dispenser a solution consisting of water for injection in a dosage of 1 ml, in which the lyophilized powder of IPH AVN peptides was dissolved in a concentration of 0.58 micrograms (mcg) per rat body weight per day for 14 days. A pipette-dispenser allowed to control the volume and the fact of liquid consumption.
The rats were killed after 14 days. Then the quadriceps muscle of the left limb was removed, fixed by immersion in a solution of 4% paraformaldehyde in phosphate buffer (PBS pH = 7.3) for 24 hours at a temperature of 4 °C. We produced slices with a thickness of 20 µm using cryotome of Leica CM 1510S model (Germany). Then the sections were mounted on a slide and stained with hematoxilin and eosin. We used the Olympus IX81 microscope for the study. The Danet criterion was used to assess the reliability of the difference in the results obtained in the groups before the application of the peptide, compared with the groups after the application of the peptide IPH AVN.
The clinical studies of the peptide IPH AVN were conducted in 98 patients aged 30 to 58 years (mean age was 41.1±1.2 years). Inclusion criteria: patients with compensated pathologies. Exclusion criteria: acute diseases, patients with decompensated pathology, patients with exacerbation of chronic diseases. We conducted studies the effectiveness of peptides in the dosage of 50 µg (n= 95 people) and 150 µg (n=92 people) to assess the effectiveness of the dose of 100 µg (n=98 people) for the peptide IPH AVN. The peptide IPH AVN was administered orally: 1 capsule (100 µg peptide) 1 time per day for 30 days, then 30 days a break in the medication. And repeat the same course for another 30 days, again 30 days a break in the medication – and the third course for 30 days. The total course was 6 months (3 courses of 30 days and 3 a break in the medication of 30 days). We studied the effectiveness of the improved management scheme of such patients using the peptide IPH AVN after 3 and 6 months. The control values was selected the results before the study. We have carried out the assessment of peripheral circulation, have assessed peripheral blood flow. Changes in regional blood flow parameters were performed in parallel sections of the right and left thighs at the same time of day (in the morning at 9-11 o’clock). Vascular elasticity was evaluated using a two-channel clinical version of Angioscan-01 (program – SI – Stiffness Index). The vascular stiffness index was measured in meters per second using the formula [path length (meters)/ reflected wave arrival time (seconds)].
We used standard statistical methods of medical and biological research.
Results and discussion. The biological analysis of angioprotective effects of the peptide IPH AVN on cell culture.
In figure 1, we show that the peptide IPH AVN significantly increases the expression of the complex of ACE, AGT, AGTR2, NOS3, MTHFR genes responsible for the normal formation and formation of the vascular system, in particular, regulating the tone of blood vessels, the smooth muscle of the vascular wall and the processes of thrombosis.
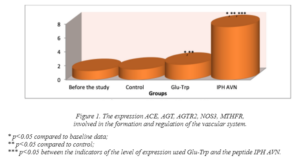
Thus, the influence of the peptide IPH AVN in human cell culture there is a statistically significant increase in the expression of genes responsible for the ontogenesis of the vascular system. These data show that the peptide IPH AVN significantly increases in human cell culture “cascade” of signal molecules, which is necessary for the activation of proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in the cells of the vascular system, the formation of vascular system, regulation of
Thus, the influence of the peptide IPH AVN in human cell culture there is a statistically significant increase in the expression of genes responsible for the ontogenesis of the vascular system. These data show that the peptide IPH AVN significantly increases in human cell culture “cascade” of signal molecules, which is necessary for the activation of proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in the cells of the vascular system, the formation of vascular system, regulation of metabolism in epithelial cells, regulation of blood vessel tone, smooth muscle of the vascular wall and thrombosis.
The figure 2 shows that the application of the peptide IPH AVN increases the expression of the VEGF protein in 4.5 times from the initial level, which is a factor in the growth of vascular endothelium.
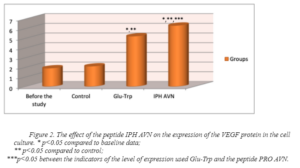
Thus, the application of the peptide IPH AVN has a pronounced angioprotective nature, in particular, induces differentiation of polypotent myogenic cells in the direction of normal formation of the vascular system and stimulates vasculogenesis (formation of the embryonic vascular system) and angiogenesis (growth of new vessels in the existing vascular system).
The effect of the peptide IPH AVN on the expression of p53 protein in cell cultures is presented in figure 3. The application of the peptide IPH AVN increases the production of protein p53, which is a transcriptional factor and acts as a suppressor of malignant tumor formation by the way of activating apoptosis in the tissues. This results lead to the conclusion about the antitumor properties of the peptide IPH AVN.
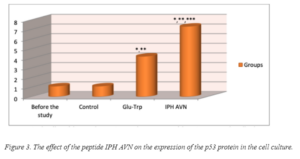
* p<0.05 compared to baseline data;
** p<0.05 compared to control;
***p<0.05 between the indicators of the level of expression used Glu-Trp and the peptide IPH AVN.
P53-dependent apoptosis also avoids the accumulation of mutations. In the case when mutations have already arisen, p53-dependent apoptosis allows to eliminate this potentially dangerous cells. On this fact, we can make a conclusion about the cytoprotective effect of the peptide IPH AVN.
The peptide IPH AVN had a high onco-protective activity in relation to the cells of the vascular system according to the expression of biological molecules in cell culture.
Biological analysis of angioprotective effects of the peptide IPH AVN in an experimental model
In the sections of the quadriceps muscle of the rats of the control group, ischemic foci were detected in the volume of 75.3±1.2% of the spread from all areas and thrombosis foci in the volume of 66.7±1.2% of the spread from all areas. While in rats of the main group ischemia foci were revealed in 2.3 times significantly less than in rats of the control group, which was 33.2±0.9% of the total area and significantly less than in 1.8 times the thrombosis foci in the volume of 36.2±1.2% of the total area, p<0.05 compared with the control group. This fact proves that the application of the peptide IPH AVN promotes to repair of the vascular bed after injury, reduce thrombosis on the basis in experimental model.
In the study of the capillary bed, we found that there were areas of necrotic endothelial cells, the accumulation of amyloid plaques in rats of the control group. All these morphological parameters indicate a sharp decrease in reparative capabilities within cells. The sites of necrotic endotheliocytes and accumulation of amyloid plaques in rats of the main group were found in 1.6 times less. These data confirm that the application of the peptide IPH AVN promotes angiogenesis in case of damage to the arterial system.
We studied the cross-sectional area of the arterial system to assess the normalizing effect of the peptide IPH AVN (figure 4).
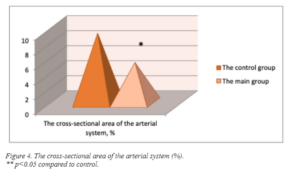
Thus, we found that in rats after the application of the peptide IPH AVN, the cross-sectional area of the arterial bed was in 1.8 times less than in rats of the control group. There is given the sharp decrease in the reparative capabilities of epithelial cells, it can be concluded that such a decrease in the area of the arterial bed indicates a lower need for compensatory reactions, which are manifested by an increase in the cross-sectional area of blood vessels in case of damage and confirm the high reparative activity of the peptide IPH AVN in relation to the ability to repair damage to the vascular wall.
Accordingly, the peptide IPH AVN has angioprotective effect and increases the adaptive capacity of endothelial cells in rats with damage to the arterial system according to experimental study.
Clinical analysis of angioprotective effects of the
peptide IPH AVN
The results of a clinical study of the application of the peptide IPH AVN showed that in people in 3 months after the application of this peptide significantly improved peripheral blood circulation parameters, namely the parameters of the rheographic index and regional minute pulse blood volume. These indicators prove the fact that the application of the peptide IPH AVN leads to the optimization of vascular function and improvement of peripheral hemodynamic parameters (table 1).
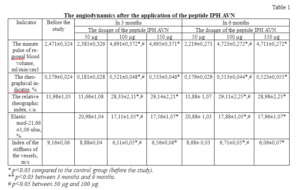
The elastic modulus decreased in 1.2 times after the application of the peptide IPH AVN. These data indicate the properties of the peptide IPH AVN, manifested in the normalization and improvement of vascular tone.
The vascular stiffness index decreased in 1.5 times after the application of the peptide IPH AVN and reached the median value of the norm. This proves that the application of the peptide IPH AVN improves the elasticity of the vascular wall, leads to the optimization of the functional activity of the peripheral circulation system.
It should be noted that the most positive reliable results in relation to the functional activity of the circulatory system were found after 3 months and remained throughout the study.
We haven`t found significant differences between the results in the application of 100 mcg and 150 mcg in all the studied parameters like in 3 months as in 6 months. Also, we have not found significant differences between the indicators in the application of 50 mcg and before the study on all parameters. This fact proves that the effective optimal dosage for the peptide IPH AVN is 100 mcg.
The performed studies confirm the high biological activity of the peptide IPH AVN in relation to the control of the normal formation of the vascular system in humans at the genetic level according to the expression of genes responsible for the ontogenesis of the vascular system, for the normal formation and formation of the vascular system, in particular, regulating the tone of blood vessels, the smooth muscle of the vascular wall and the processes of thrombosis. The application of the peptide IPH AVN significantly increases in human cell culture “cascade” of signal molecules, which is necessary for the activation of proliferation and differentiation of stem cells in the cells of the vascular system, the formation of vascular system, regulation of metabolism in epithelial cells, regulation of blood vessel tone, smooth muscle of the vascular wall and thrombosis. The application of the peptide IPH AVN has a pronounced angioprotective nature, in particular, induces differentiation of polypotent myogenic cells in the direction of normal formation of the vascular system and stimulates vasculogenesis (formation of the embryonic vascular system) and angiogenesis (growth of new vessels in the existing vascular system). The data indicate a high onco-protective activity of the peptide IPH AVN against cells of the vascular system according to the expression of biological molecules in cell culture.
It was also proven that the application of the peptide IPH AVN promotes the reparation of the arterial system after damage, reduce clot formation on the basis of these experimental models. The application of the peptide IPH AVN promotes angiogenesis in case of damage to the arterial system. The peptide IPH AVN has a high reparative activity in relation to the ability to repair damage to the vascular wall. The peptide IPH AVN has an angioprotective effect and increases the adaptive capacity of endothelial cells in rats with damage to the arterial system according to experimental study.
Thus, the application of the peptide IPH AVN leads to the optimization of vascular function and improvement of peripheral hemodynamics. We also obtained data on the properties of the peptide IPH AVN, manifested in the normalization and improvement of vascular tone. The application of the peptide IPH AVN improves the elasticity of the vascular wall, leads to the optimization of the functional activity of the peripheral blood circulation system according to clinical study.
The application of peptide IPH AVN recommended in the form of biologically active food additives to improve the functional activity of the circulatory system, indicators of peripheral hemodynamics, microcirculation.
With the support of «Ideal Pharma Peptide GMBH», Ferdinandstr. 11 61348 Bad Homburg.
 IPH – PEPTIDES
Read more
IPH – PEPTIDES
Read more