
Bladder dysfunction in the elderly is a significant public health issue. Laboratory studies using animal models have thus far failed to provide new clinically useful information. Demographic and urodynamic studies in elderly patients reveal that neurological diseases and obstruction of the bladder outlet are the primary causes of urination dysfunction. The impact of aging per se on the bladder is unknown. Elderly patients with bladder dysfunction should undergo a thorough history taking and physical examination combined with a practical assessment of urodynamics, rather than simply being labeled as having “bladder dysfunction in the elderly.”
Overactive bladder is a disorder of the storage function of the lower urinary tract, which is more common in the elderly. With demographic forecasts predicting an increase in the proportion of people over 65 worldwide, it is reasonable to expect that the health care burden associated with this condition will also increase. The pathophysiology of overactive bladder in the elderly is believed to be multifactorial, with disturbances in nervous supply and/or the structure/function of the urothelium or bladder smooth muscle leading to bladder hypersensitivity, bladder sensation disorders (urgency), and involuntary detrusor contractions. The potential for an elderly patient to have several comorbidities means that a thorough characterization of their overall condition is required before deciding on the most appropriate treatment option for their urinary tract pathology.
Consequently, scientists, doctors, and researchers are increasingly concerned with finding new means to protect urological health and improve the quality of life for the elderly, searching for so-called bladder cytoprotectors.
IPH VGA Peptide Complexes are the latest developments in cell and tissue protection. A lack of building materials, which peptides can provide, negatively affects urological health, reduces oncological protection and immunity, leading to the development of various diseases.
This article presents a brief overview of the research findings on the effects of using the IPH VGA peptide, which are cytoprotectors of the aging bladder and can enhance life quality by improving its function, thus offering additional preventive benefits.
Increased levels of local and systemic biomarkers, which are released upon peptide application and have protective properties, indicate that their use is important from the perspective of organ function preservation and restoration at any life stage and in any diseases.
Objective: to study the possibilities of the IPH VGA peptide complex.
To assess the cytoprotective properties of the peptides, we studied the expression of genes responsible for bladder formation, namely CYP1A1, GSTM1, GSTP1, and the DNA repair gene XRCC1.
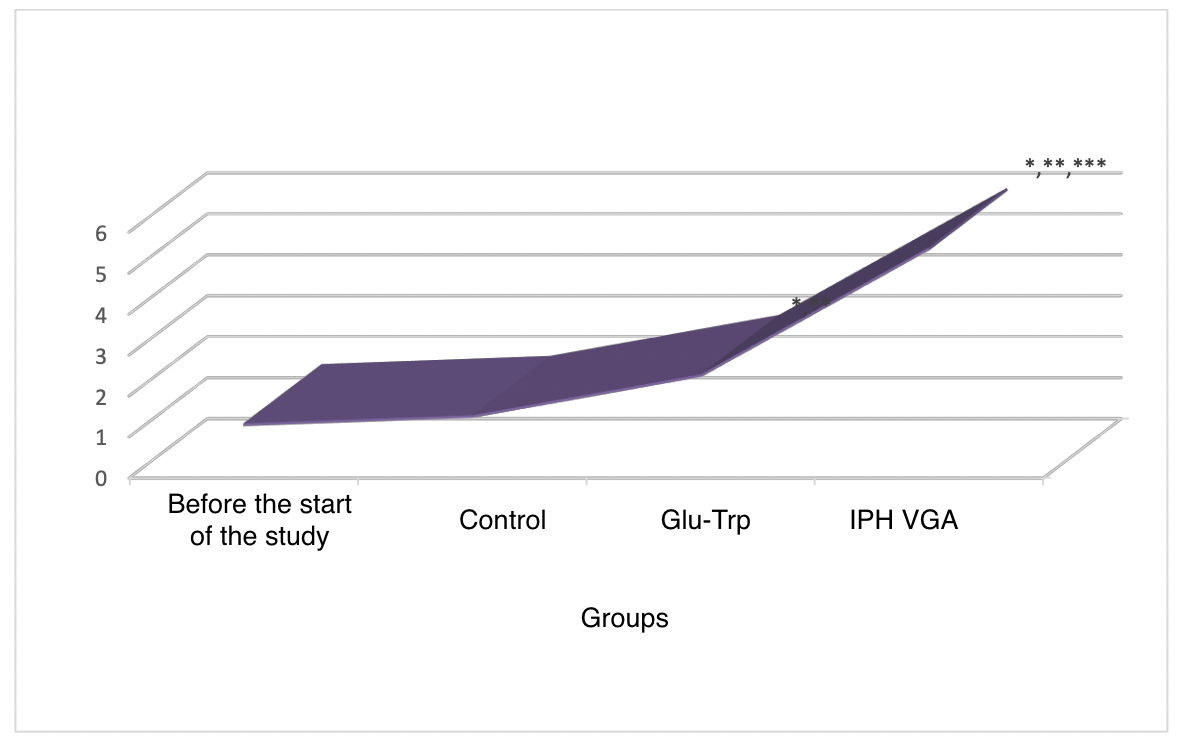
Figure 1. The Effect of the IPH VGA Peptide on the Expression of Genes CYP1A1, GSTM1, GSTP1, and the DNA Repair Gene XRCC1.
The study showed that the IPH VGA peptide’s recognition of the genetic apparatus provides protection against pathogens and controls the development of pathological changes concerning the bladder. This is expressed in the cytoprotective action concerning the bladder and its function, as it positively affects the synthesis of the genes CYP1A1, GSTM1, GSTP1, and the DNA repair gene XRCC1.
Fibroblast growth factors (FGF) and their receptors control a wide range of biological functions, regulating cellular proliferation, survival, migration, and differentiation. Although targeting FGF signaling as a therapeutic target for cancer treatment is behind other receptor tyrosine kinases, there is substantial evidence of the importance of FGF signaling in the pathogenesis of various tumor types, and clinical agents are being developed that specifically target FGFs or FGF receptors. FGF signaling can stimulate oncogenesis, but in different contexts, FGF signaling can mediate protective functions of the tumor. Identifying the mechanisms underlying these differential effects will be important for understanding tumor progression and increasing protection against oncological processes. Therefore, this protein was chosen as a marker to evaluate the cytoprotective action of the IPH VGA peptide.
According to Figure 2, the IPH VGA peptide has a potent oncoprotective and cytoprotective action, as it can reduce the level of fibroblast growth factor expression by 81.8±1.3%.
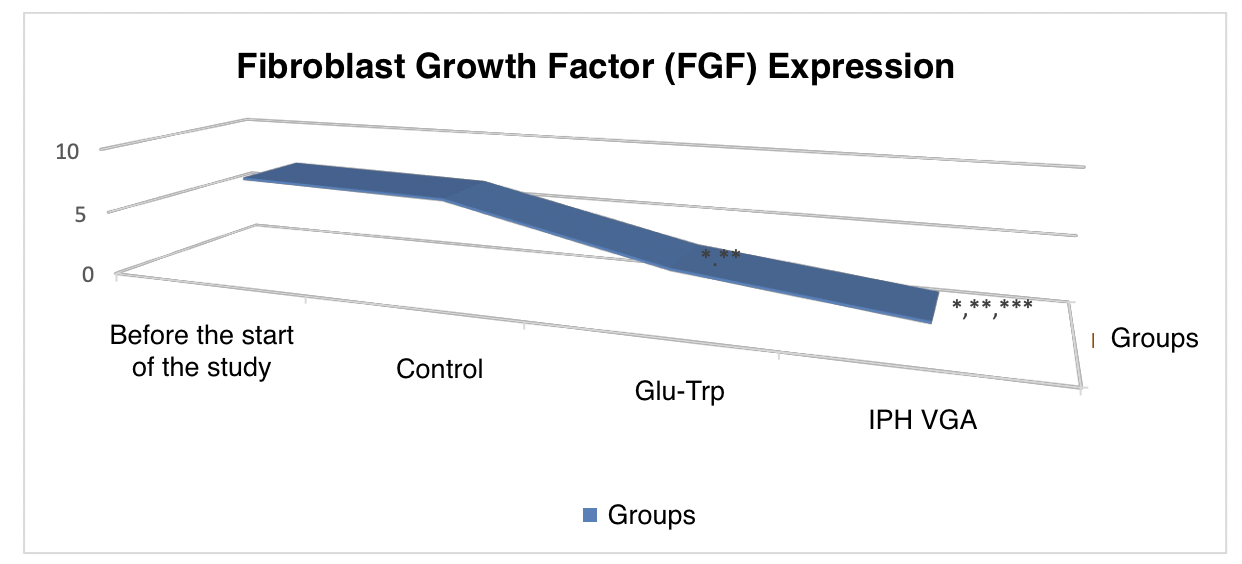
Figure 2. The Effect of the IPH VGA Peptide on the Expression of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF).
Consequently, the proven cytoprotective effect of the IPH VGA peptide allows us to conclude that it has a high oncoprotective function, which is expressed in protecting the body from increased expression of oncogenic markers.
Bladder dysfunction encompasses a spectrum of lower urinary tract symptoms that significantly deteriorate an individual’s quality of life. When one is unable to completely empty the bladder, there’s a risk of long-term damage to the bladder and kidneys, potentially leading to infectious processes.
We studied urodynamic indicators and found that after applying the IPH VGA peptide, the frequency of daytime urination decreased by 45.6±1.2%, the degree of abdominal pressure by 33.5±0.8%, and the time to reach maximum urination speed by 65.6±1.3%. This demonstrates the high cytoprotective function of the VGA peptide concerning bladder function.
The data are presented in Table 1.
Table 1 Effect of the IPH VGA Peptide on Bladder Function
|
Indicator
|
Before the Study
|
After 3 Months | After 6 Months | ||||
| Dosage of Peptide | Dosage of Peptide | ||||||
| 50 µg | 100 µg | 150 µg | 50 µg | 100 µg | 150 µg | ||
| Frequency of Daytime Urination | 8.7±0.2 | 8.5±0.2 | 7.1±0.3*,# | 7.2±0.3* | 8.8±0.2 | 6.2±0.1*, **, # | 6.1±0.1*, ** |
| Abdominal Pressure Level (points) | 3.2±0.4 | 3.3±0.4 | 2.8±0.3 | 2.6±0.3 | 3.4±0.4 | 2.2±0.3 | 2.1±0.3 |
| Time to Reach Maximum Urination Speed (ml/s) | 3.7±0.7 | 3.6±0.7 | 2.5±0.6*,# | 2.6±0.6* | 3.8±0.7 | 1.1±0.1*,# | 1.2±0.1* |
p<0.05 between indicators compared to the control group (before the study).
** p<0.05 between indicators after 6 months and 3 months.
# p<0.05 between indicators when applying 50 µg and 100 µg.
Thus, the recognition by the IPH VGA peptide of the genetic apparatus provides protection against pathogens and controls the development of pathological changes in the bladder. This is manifested in the cytoprotective action concerning the bladder and its function, positively affecting the synthesis of the genes CYP1A1, GSTM1, GSTP1, and the DNA repair gene XRCC1. The IPH VGA peptide possesses potent oncoprotective and cytoprotective actions, as it can reduce the level of expression of the fibroblast growth factor by 81.8±1.3%. The proven cytoprotective effect of the IPH VGA peptide indicates a high oncoprotective function, which is manifested in protecting the body from increased expression of oncogenic markers. The IPH VGA peptide has an anti-inflammatory cytoprotective action regarding inflammatory diseases of the urogenital system, particularly the bladder. After applying the IPH VGA peptide, the frequency of daytime urination decreased by 45.6±1.2%, the degree of abdominal pressure by 33.5±0.8%, and the time to reach maximum urination speed by 65.6±1.3%, proving the high cytoprotective function of the VGA peptide concerning bladder function.
1. Ilnickii A.N., Prashchayeu K.I. Neujazvimye. Kniga o zdorov’e [Invulnerable. The book about health]. M.: Diskurs [Discourse]. 2021, 336 p. (In Russian).
2. Serrano-Aroca Á, et al. Bioengineering Approaches for Bladder Regeneration. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29914213 Free PMC article. Review.
3. Pokrywczynska M, et al. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). Human urinary bladder regeneration through tissue engineering – an analysis of 131 clinical cases. 2014. PMID: 24419462 Review.
4. Song L, et al. Bladder acellular matrix and its application in bladder augmentation. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2014. PMID: 23895225 Review.
5. Pokrywczynska M, et al. Urinary bladder augmentation with acellular biologic scaffold-A preclinical study in a large animal model. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2022. PMID: 34323358