
The main function of the pineal gland in the brain is the production of endogenous melatonin, the reduction of which depends on many factors of the modern world. Thus, the constant action of oxidative stress, which develops from external influences and is exacerbated by the development of diseases, psycho-emotional stress, and disorders in the body, including the development of metabolic syndrome symptoms, leads to a reduction in the level of endogenous melatonin.
The aforementioned factors affect the shortening or damage of telomeres, reduction in the synthesis of growth factors, expression of proteins p53, pRb, leading to cellular aging, apoptosis, DNA repair, and genome instability. These factors are precursors of both premature aging and the development of oncological formations.
Therefore, when studying the properties of the pineal gland, we selected markers that characterize its action and properties.
The level of melatonin is determined by its metabolite in morning urine – 6-hydroxysulfate melatonin, which is the most reliable indicator of this hormone. The data are presented in Table 1.
Table 1. Dynamics of tau protein expression with the use of the peptide IPH EP in the long term
| Age Group | Normal Values (ng/h) | 3 Months Without IPH EP | 3 Months With IPH EP | 6 Months Without IPH EP | 6 Months With IPH EP | 1 Year Without IPH EP | 1 Year With IPH EP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adults (20-35 years) | 1017 – 6074 | 2444.9±5.3 | 4574.8±6.8* | 2556.8±5.8 | 5008.0±6.9* | 2262.3±4.7 | 6062.3±7.7* |
| Adults (36-50 years) | 598 – 3612 | 1459.9±3.7 | 2998.2±5.7* | 1789.2±3.9 | 3124.5±5.9* | 1896.2±4.7 | 3278.2±6.6* |
| Adults (51-65 years) | 861 – 2421 | 1042.5±3.2 | 1784.9±4.3* | 1056.2±3.4 | 1984.4±4.3* | 1009.2±2.2 | 2138.2±4.6* |
| Adults (over 65 years) | 327 – 2396 | 456.9±1.3 | 1075.2±1.7* | 562.9±1.8 | 1678.2±1.7* | 561.7±1.2 | 2145.1±1.8* |
*p<0.05 between indicators without the use of the peptide and with the use of the peptide IPH EP.
The level of melatonin in patients aged 20 to 35 years was below the median normal value, likely due to the dense work schedule of this age group affecting the quantity and quality of sleep, leading to a reduction in the production of endogenous melatonin. However, the use of the peptide IPH EP contributes to the restoration of endogenous melatonin production, which amounted to 4574.8±6.8 ng/h after 3 months, 5008.0±6.9 ng/h after 3 months, and maximally close to the upper limit of normal results – 6062.3±7.7 ng/h after 1 year, p<0.05 between indicators without the use of the peptide and with the use of the peptide IPH EP. A similar trend towards the level of endogenous melatonin approaching the lower boundaries of normal values was observed in other age groups, but with a lesser tendency in patients who did not use the peptide IPH EP, and a significant positive trend in increasing the level of endogenous melatonin by 39.2-48.9% after the use of the peptide IPH EP in all age groups.
Protein p53 controls the course of cellular cycle processes and the absence of damages in the genome that could lead to further pathology development. Protein p53 is activated only when the cell is subjected to various stresses, such as telomere loss, DNA damage, oncogene activation, and oxidative stress, leading to premature aging. Thus, p53 is a factor that initiates the transcription of a group of genes and is activated when DNA damage accumulates. In the absence of genetic apparatus damage, the p53 protein remains inactive. The function of the p53 protein is to remove from the replicating cell pool those cells that are potentially oncogenic.
Therefore, we studied the expression of the p53 protein after the use of the peptide IPH EP. The data are presented in Figure 2.
During the experiment, it was proven that the use of the peptide IPH EP increases the expression of the oncosuppressor protein p53 by 61.9%, as shown in the microscopy results in Figure 2. These data indicate the high oncoprotective and antioxidant function of the peptide IPH EP concerning the entire organism.
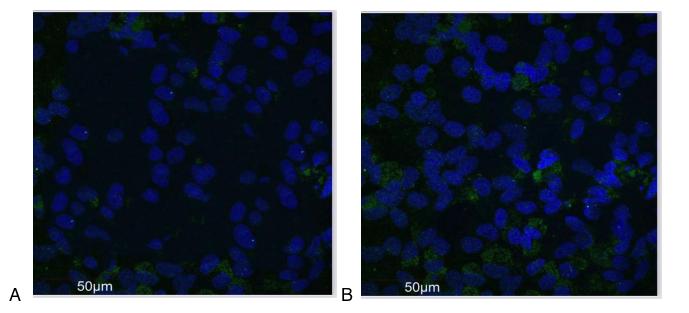
Figure 2. Expression of p53 protein (green fluorescent glow, microscopy, 400×350)
A – without the use of the peptide, B – with the use of the peptide IPH EP.
To determine biological age as a regulator of reserve capabilities and functionality of the organism in terms of controlling the level of melatonin, we tested the levels of aging markers protein sirtuin Sir2, which are involved in gene regulation and prevent DNA damage, and protein 16INK4a, which is a biological marker of the onset of carcinogenesis – its increased expression is observed in precancerous changes and varies with age (Figure 2), in the buccal epithelium of patients of different ages (group of patients without the use of the peptide IPH EP – from 35 to 55 years: average age 43.4±1.2 years, group of patients without the use of the peptide IPH EP – from 35 to 55 years: average age 43.4±1.2 years,), data are presented in Table 2.
The use of the peptide IPH EP contributes to the restoration of the level of sirtuin aging proteins, which amounted to 477.7±1.2 U after 3 months, 585.6±1.2 U after 3 months, and maximally close to positive results – 679.7±1.3 U after 1 year, p<0.05 between indicators without the use of the peptide and with the use of the peptide IPH EP. The use of the peptide IPH EP contributes to the reduction of the expression area of mRNA p16INK4a, which amounted to 4.9±0.5% after 3 months, 2.2±0.6% after 3 months, and maximally close to positive results – 0.9±0.01% after 1 year, p<0.05 between indicators without the use of the peptide and with the use of the peptide IPH EP. A similar trend towards regulating the reserve capabilities and functionality of the organism proves a significant positive trend in increasing the body’s reserve forces by 49.1-57.2% after the use of the peptide IPH EP in the long term.
Table 2 The level of expression of aging markers (sirtuins Sir2 and p16INK4a) depending on the use of the peptide IPH EP in the long term
| ging Markers | 3 Months Without IPH EP | 3 Months With IPH EP | 6 Months Without IPH EP | 6 Months With IPH EP | 1 Year Without IPH EP | 1 Year With IPH EP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sir2 Protein Level (units) | 287.7±1.2 | 477.7±1.2* | 286.3±1.4 | 585.6±1.2* | 276.2±1.2 | 679.7±1.3* |
| mRNA p16INK4a Expression Area (%) | 9.1±0.7 | 4.9±0.5* | 7.9±0.8 | 2.2±0.6* | 7.2±0.5 | 0.9±0.01* |
*p<0.05 between indicators without the use of the peptide and with the use of the peptide IPH EP.
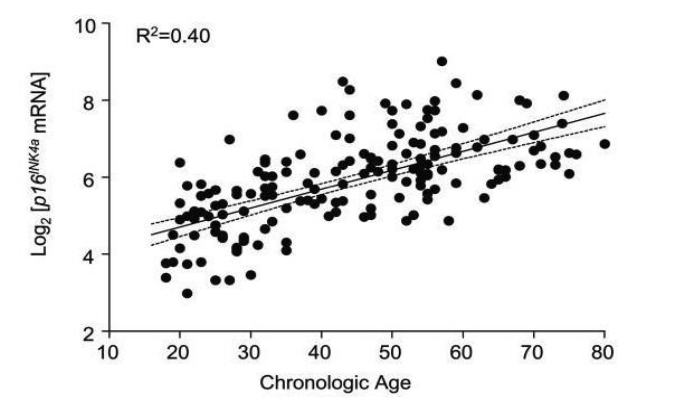
Figure 3. Age-dependent expression of mRNA p16INK4a [8]
To confirm this hypothesis, we constructed a detailed curve of the dynamics of mRNA p16INK4a expression (%) depending on the time of use of the peptide IPH EP at a dosage of 100 mcg as effective and optimal for this peptide (Figure 4).
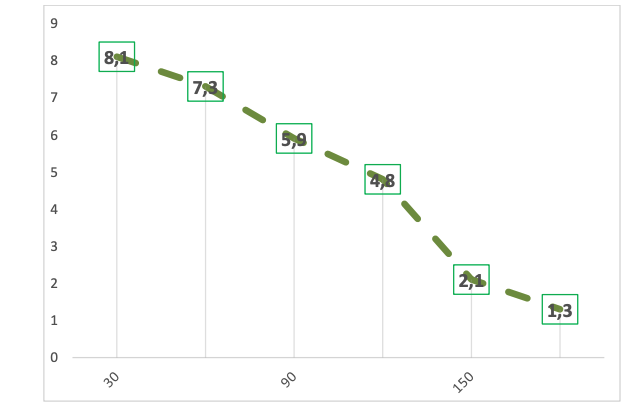
Figure 4. Expression of mRNA p16INK4a (%) depending on the time of use of the peptide IPH EP at a dosage of 100 mcg as effective and optimal for this peptide
Legend:
On the X-axis – time intervals (days);
On the Y-axis – the area of expression of mRNA p16INK4a (%).
The dynamics of the expression area of mRNA p16INK4a significantly decreased in a geometric progression 90 days after the use of the peptide IPH EP, confirming the oncoprotective and anti-aging action of the studied peptide.
Additionally, we conducted a comparative analysis of the expression of the aging protein Sir2 in microscopy in patients before the use of the peptide IPH EP and 3 months after the use of the peptide IPH EP (Figure 5).
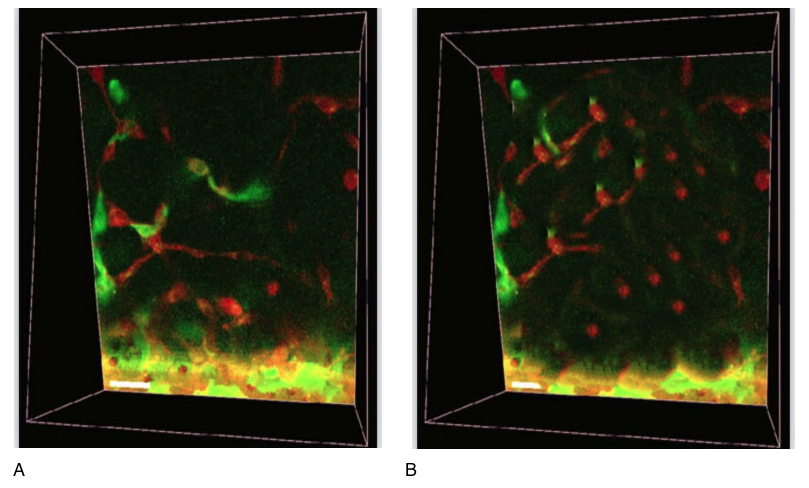
Figure 5. Expression of sirtuin protein (red fluorescent glow of nuclei, microscopy, 400×350, 3D modeling).
A – before the use of the peptide,
B – 3 months after the use of the peptide IPH EP.
The obtained data confirm the fact that the use of the peptide IPH EP contributes to the slowing down of aging processes by 39.8%, increasing biological age, and acts as a regulator of reserve capabilities and functionality of the organism, which is confirmation of possessing high anti-aging function, oncoprotective function, and a high ability to increase the reserve resilience of the organism after the use of the peptide IPH EP in the long term.
Serotonin – the hormone of joy, mood, stable psycho-emotional state. Through certain biochemical reactions, the hormone melatonin is formed from serotonin. Therefore, the pineal gland’s influence on mood, anxiety-depressive disorders is direct.
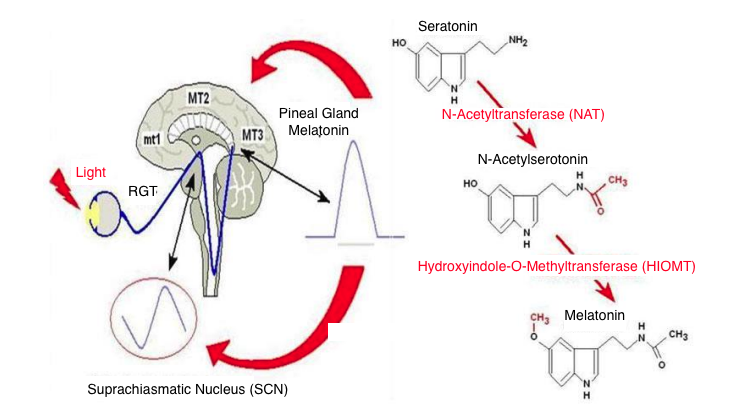
Figure 6. Biochemical reactions of the synthesis of the hormone melatonin from serotonin
The clinical impact of the peptide IPH EP as a regulator of reserve capabilities and functionality of the organism in terms of controlling the level of melatonin was studied by us from a clinical point of view in terms of anxiety level in patients of different ages (35-49 years: average age: 39.9±1.2 years, n=42 people).
Using the personal scale of the Spielberger-Hanin test, we found that before the start of the study, there was a significantly higher level of anxiety due to the personal component compared to patients after the use of the peptide IPH EP 3 months later – 52.3+1.9 points (high anxiety) and 33.2+1.5 points (borderline value between low and medium anxiety), respectively, and a significant reduction was also noted 6 months later to normal values bordering between mild anxiety and absence (Figure 7).
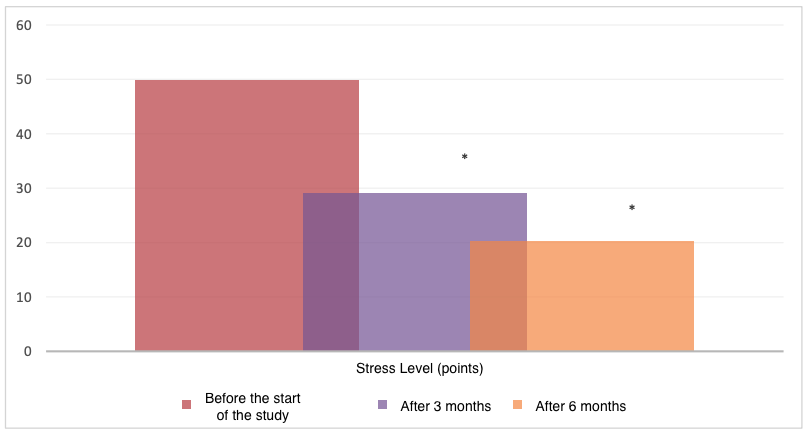
*p<0.05 between indicators compared to indicators before the start of the study.
Figure 7. Anxiety level (points, M±m)
The obtained data confirm the fact that the use of the peptide IPH EP contributes to a reduction in the level of anxiety by 58.9%, confirming its clinical efficacy as a regulator of reserve capabilities and functionality of the organism.
Further, an assessment was made of the psychological and physical components of the quality of life and the impact of the use of the peptide IPH EP on the functionality of the organism.
Before the start of the study, attention was drawn to the low indicators of mental and emotional health components, which reduces the psychological component of health and is likely related to the high level of anxiety and reduced level of melatonin in the studied patients (Figure 8).
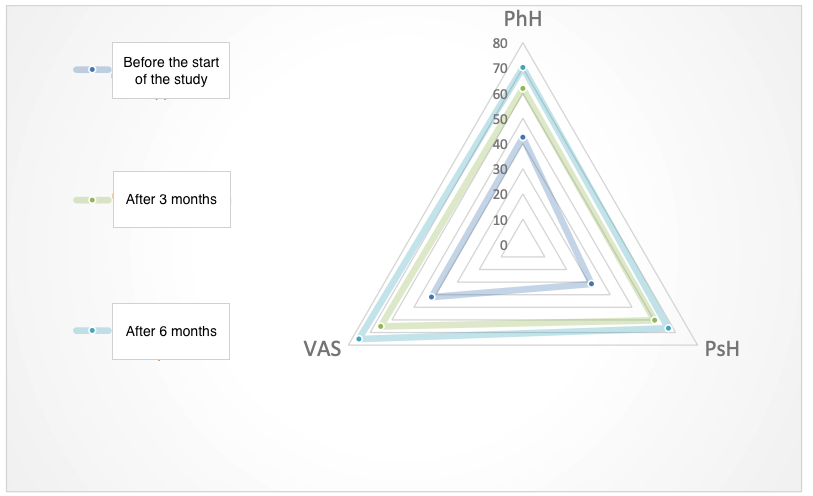
Figure 8. Dynamics of physical and psychological components of the quality of life (points, M±m)
However, the subsequently obtained data confirm the fact that the use of the peptide IPH EP contributes to an improvement in the quality of life by 53.2% from the psychological component and by 39.7% from the physical component, confirming the fact that the peptide IPH EP acts as a regulator of reserve capabilities and functionality of the organism, possesses a high ability to reduce anxiety and improve the psychological component of the quality of life in the long term.